PVC is essentially a polymer made by polymerizing vinyl chloride monomers. While it is a robust material, its polymeric structure makes it susceptible to degradation through dehydrochlorination, especially when subjected to heat or UV radiation. This degradation can compromise the mechanical properties of the material, making it brittle and reducing its lifespan. Furthermore, it may release hydrochloric acid (HCl), which can be corrosive to metal components. Therefore, stabilizers are essential to maintain the long-term performance of PVC products.
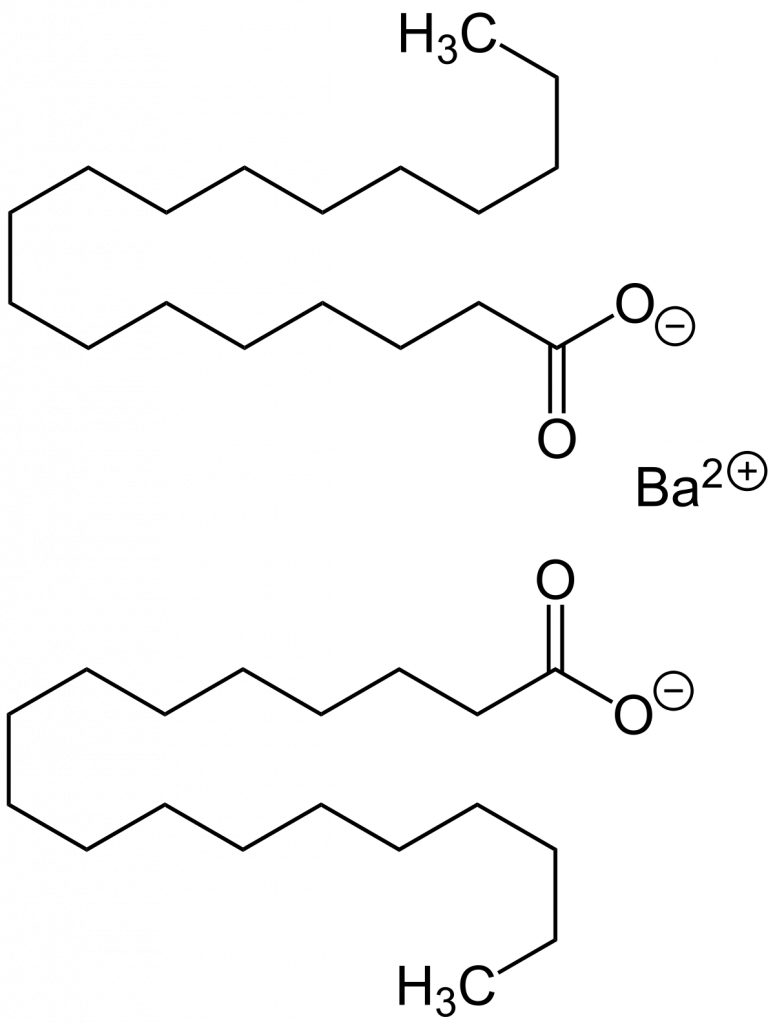
Barium stearate is an organometallic compound formed by the reaction of stearic acid with barium salts. The molecule is generally represented as (C17H35COO)2Ba. It is a white, waxy solid at room temperature and is hydrophobic, meaning it does not mix well with water. It is also highly thermally stable, a property that makes it particularly suitable for use as a PVC stabilizer.
Mechanism of Action (Barium Stearate in Rigid PVC)
Stabilization
When PVC degrades, one of the byproducts is hydrochloric acid. Barium stearate acts as an acid scavenger, effectively neutralizing the hydrochloric acid. This is crucial because the presence of free HCl would accelerate the degradation process further, creating a vicious cycle.
Lubrication
Barium stearate also serves as a lubricant during the PVC production process. PVC manufacturing often involves high-temperature processing, and the polymeric chains can experience high levels of friction. Barium stearate eases this friction, making the manufacturing process smoother and reducing wear and tear on machinery.
Synergistic Effects
While barium stearate is effective on its own, it often operates in conjunction with other stabilizers like cadmium stearate or zinc stearate for enhanced performance. Such combinations offer more comprehensive protection against both short-term and long-term degradation mechanisms.
Applications of Barium Stearate-Stabilized Rigid PVC
Construction and Infrastructure
The most prominent application lies in the construction industry, particularly in plumbing solutions. PVC pipes treated with barium stearate have a significantly longer operational life. They also resist the corrosive action of chemicals and high-temperature water flow.
Electrical Installations
In electrical conduits, the insulation properties of PVC are paramount. The addition of barium stearate not only adds to its stability but also ensures the material retains its insulating properties over an extended period.
Automotive and Transportation
Manufacturers use rigid PVC to create various automotive components. The presence of barium stearate ensures that these components can withstand the thermal and mechanical stresses experienced in automotive applications.
Safety and Regulatory Implications
You should not use barium stearate in products that come into direct contact with food or water intended for human consumption, although it’s generally safe for many other applications. This is because barium compounds can be toxic when ingested in large quantities.Regulatory agencies have established standards that limit the amount of barium stearate you can use in specific applications.
Conclusion (Barium Stearate in Rigid PVC)
Barium stearate plays an indispensable role in the stabilization of rigid PVC. Its dual action as both a stabilizer and a lubricant makes it an invaluable additive in the PVC industry. By enhancing the material’s resistance to thermal and UV degradation, barium stearate extends the functional life of PVC products. However, it is essential to adhere to safety guidelines and regulations, considering the potential toxicity of barium compounds. The importance of additives like barium stearate in ensuring the longevity and functional integrity of PVC, which we use extensively for various applications, cannot be overstated.