Calcium stearate, a carboxylate of calcium, exists as a waxy powder, flakes, or granules. Predominantly used as a lubricant, stabilizer, or flow agent in numerous applications from plastics and rubber processing to the food and pharmaceutical industries, calcium stearate is not just another compound. It holds an important position in modern industrial practices. This article aims overview of calcium stearate’s chemistry, production methods, applications, and its impacts on human health and the environment.
Chemical Properties
Chemically, calcium stearate is an organic compound with the molecular formula [C18H35O2]2Ca[C18H35O2]2Ca. It is an ionic compound featuring a calcium cation (Ca2+Ca2+) and stearate anions (C18H35O2−C18H35O2−). Anion is derived from stearic acid, a long-chain fatty acid.
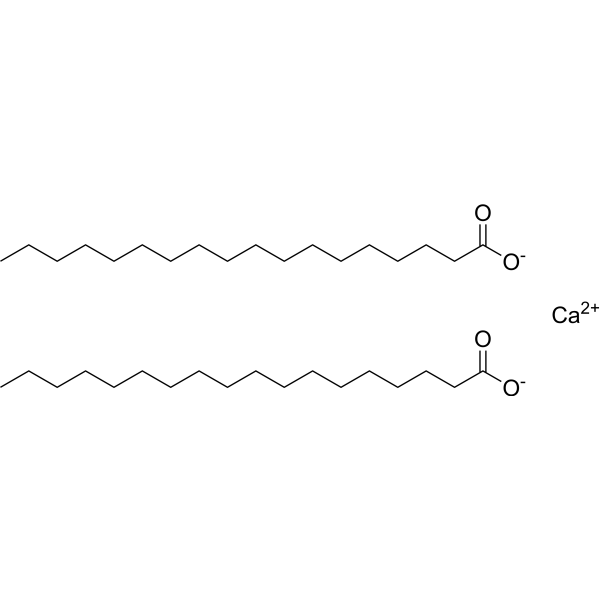
Stability and Solubility
Calcium stearate is relatively stable under normal conditions. However, it decomposes into stearic acid and calcium salts upon heating. Solubility is an interesting aspect of calcium stearate; it’s practically insoluble in water, alcohols, and ether but dissolves in hot pyridine.
Production Methods
There are several methods for producing calcium stearate, which include:
- Direct Saponification: A reaction between stearic acid and calcium hydroxide or calcium oxide produces calcium stearate.2C18H35COOH+Ca(OH)2→(C18H35COO)2Ca+2H2O2C18H35COOH+Ca(OH)2→(C18H35COO)2Ca+2H2O
- Double Decomposition: It involves reacting sodium stearate with a soluble calcium salt like calcium chloride, leading to the formation of calcium stearate and sodium chloride.
- Fusion Method:. Calcium oxide is fused with stearic acid to obtain the compound. This is particularly useful for producing high-purity calcium stearate.
Applications (Applications of Calcium Stearate)
Plastics Industry
In the plastics industry, calcium stearate acts as an acid scavenger and stabilizer. Used in the production of PVC and other polymers, where it neutralizes acidic byproducts during polymerization.
Food Industry
Employed as an anti-caking agent in food processing. Common in baking powders and cheese, calcium stearate prevents agglomeration of particles.
Pharmaceuticals
It finds applications as a lubricant in tablet manufacturing, aiding in the smoother flow of tablet substances during processing.
Cosmetics
In cosmetics like makeup and skin-care products, Used for its lubricating properties.
Construction
Used as a water repellent in concrete, enhancing the durability and mechanical strength of construction materials.
Human Health and Toxicity (Applications of Calcium Stearate)
Calcium stearate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices. However, overexposure might lead to minor gastrointestinal irritations.
Environmental Impact
Though considered to be low in toxicity, calcium stearate can be problematic if it enters aquatic systems in large quantities, affecting aquatic life.
Regulatory Framework
In the United States, calcium stearate is regulated by agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). In Europe, it falls under the purview of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA).
Conclusion (Applications of Calcium Stearate)
From its chemical complexities to its myriad of applications, calcium stearate is an incredibly versatile compound that facilitates various industrial processes. While it is generally safe, monitoring its use and environmental impact is crucial for sustainable practices. As a compound that has stood the test of time, calcium stearate will continue to be a critical player in modern manufacturing and beyond.
By understanding calcium stearate’s science, applications, and impacts, one gains a well-rounded perspective on why this compound is indispensable in today’s world. With ongoing research and regulatory vigilance, calcium stearate will likely continue to serve a plethora of industries while minimizing its environmental footprint.

